What is electronic manufacturing? Electronic manufacturing involves the research, development, production, and assembly of various components—including semiconductors, electronic components, sensors, power supplies, motors, interactive devices, and embedded systems—into electronic products applicable across consumer, automotive, industrial, medical, marine, and aerospace sectors.
Multifaceted Aspects of Electronic Manufacturing
- Equipment Manufacturing
Equipment manufacturing constitutes a vital segment within electronic manufacturing, encompassing apparatus for producing diverse electronic components, production lines, and testing equipment. - Digital Production
Digital production represents a significant trend in electronic manufacturing. It employs computer-integrated manufacturing systems to achieve objectives such as zero-inventory production, just-in-time supply, and on-demand manufacturing. - Internet of Things
The application of IoT technology in electronics manufacturing enables remote monitoring of production processes, automated control, and data acquisition, thereby enhancing production efficiency and quality. - Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing within electronics further leverages artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing to achieve autonomous decision-making, self-adjustment, and self-optimisation, thereby improving production efficiency and quality.
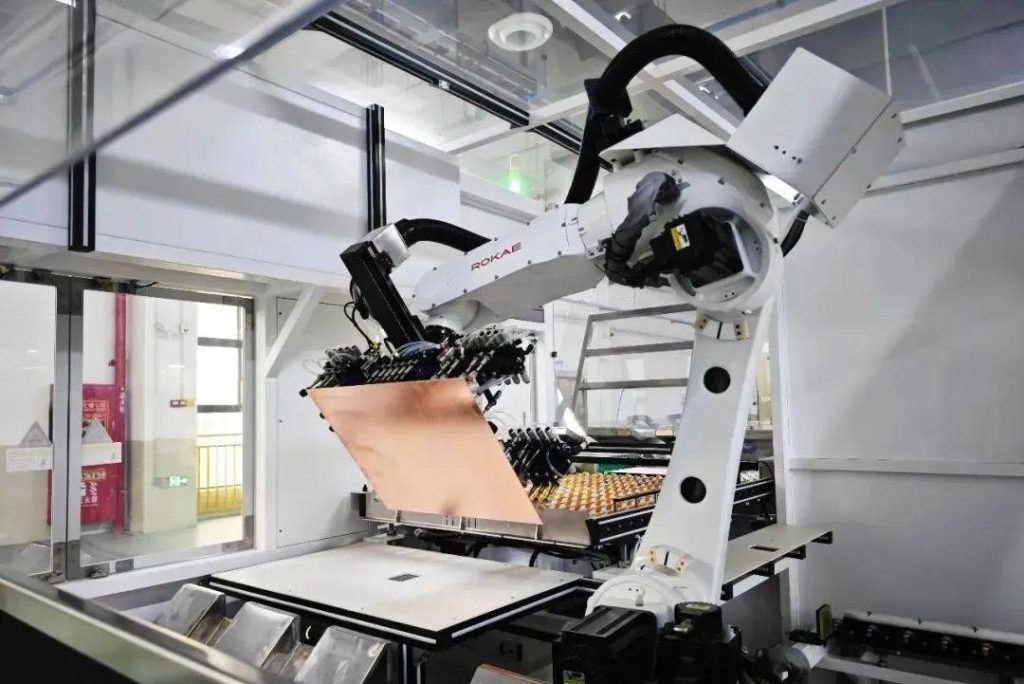

Electronics Manufacturing Process:
The production of electronic products typically encompasses multiple stages, commencing with raw material procurement and concluding with final assembly and testing. Specifically, the electronics manufacturing process comprises several key stages:
Material Procurement:
Procurement of required electronic components, printed circuit boards (PCBs), wiring, and other materials based on product design and production requirements.
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly: Employing SMT techniques to precisely mount electronic components onto PCBs. This stage relies heavily on automated equipment, significantly boosting production efficiency and assembly accuracy.
DIP Insertion: For components unsuitable for SMT placement—such as larger capacitors, resistors, or connectors—DIP (Dual In-line Package) insertion is employed. This involves manual or automated insertion of components into designated sockets.
Soldering and Securing: Following placement and insertion, wave soldering or reflow soldering processes are applied to firmly bond components to the PCB, ensuring robust connections.
Assembly and Integration: Soldered PCBs are assembled with other components—such as enclosures, displays, and buttons—to form complete electronic products.
Testing and Quality Inspection: Rigorous testing and quality inspection are conducted on the assembled electronic products to guarantee stable performance and compliance with design specifications.
Packaging and Dispatch: Products passing testing undergo packaging preparation before being dispatched to distribution channels or delivered to end-users.
As an electronics manufacturing provider and service provider, GEO possesses professional PCB design capabilities and advanced manufacturing expertise. It maintains a comprehensive quality management system and precise testing methods to guarantee product quality. Simultaneously, efficient supply chain management and internal coordination ensure smooth production. The company also prioritises technological research and development alongside innovation, delivering timely professional customer service and bespoke solutions.